Identify
Description |
Identifying the Root Causes of issues, then developing and prioritizing recommendations for immediately improving the identified Process leads to quick improvements and viable solutions. Adjusting the Process Improvement Team and developing Success Criteria assures that solutions will be successfully deployed.
Process Flow Diagram
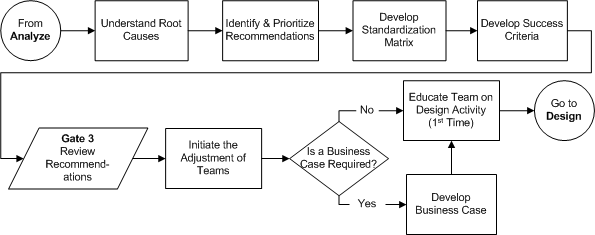
In this diagram the Team meets to understand what is causing the problems and performance issues within the existing process. The team also identifies quick fixes for immediate improvement to the process. Recommendations are made to the Process and Resource Owners who direct the team to hold or move forward to designing the “should-be” process.
Procedures
Purpose
The goal!
To explain “why the causes persist and problems have not been addressed.”
Help: Root Causes are analogous to the “base of an iceberg.”
Remember: If your team does not agree on the problem they won’t agree with the solution.
Why do it?
Root Cause identification brings hidden problems to the surface and focuses attention on the underlying mindsets that can inhibit improvement.
What to do:
As issues are identified at the activity level, ask the stakeholders the question “why, Why, WHY?” to better define the Root Cause.
Use the change level B&D’s categories to get an understanding of which breakdowns and disconnects really need study and resolve to bring about lasting improvement.
In the As-Is Worksheet, document the Cause and Root Causes aligned with the Activity level.
Decision:
Has enough information been generated to move on to Identify and Prioritize Recommendations?
Help: Do not focus attention on determining Root Causes at the Task level. Focus on the Activity level where the problem has been defined. Remember to examine root causes for Inter-Process Linkage breakdowns before moving on to recommendations.
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Existing Processes, Activities, and Tasks are documented in the As-Is Worksheet and in chronological order.
Activity Breakdowns and Disconnects have been identified and captured.
Activity Breakdowns and Disconnects have been categorized into the various Change Levels.
|
||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To agree on improvement recommendations by envisioning what is possible for the future.
Why do it?
Identifying and prioritizing recommendations enables the team to systematically consider potential possibilities, assuming that the issues, causes, and root causes are resolved through creative solutions.
What to do:
1) Identify and prioritize recommendations.
2) After recommendations are prioritized, if the team feels that the high priority recommendations will quickly benefit the organization, they can implement them immediately, assuming both the Process and Resource Owners approve. These changes should be carried forward into the “should be” documentation.
3) Brainstorm new opportunities that do not come up in the Breakdowns & Disconnects.
Decision.
Has enough information been generated to move forward?
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Root Cause identification is complete
|
||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To agree on standardized processes except where differentiation adds business value.
Why do it?
In general, it is more efficient to operate and maintain a standard process across the enterprise versus multiple variations of a given process. For example, employees engaged in pursuit of a standard business process can:
- Utilize a common system
- Receive training with a common curriculum
- Collaborate across disparate organizations to solve common problems and share common learnings
What to do:
Using the guidelines provided, the Process Improvement team decides which activities and tasks will be standardized across SBUs and functional areas, and records the results of their analysis on a Standardization Matrix. This will serve as a roadmap during the Design activity. For those that cannot be standardized, further information will be required as noted in the instructions below.
Decision:
Which activities and tasks can be standardized across the enterprise?
If differentiation is recommended, which criterion justifies and how?
Does having the activity or task different add value?
Responsibility
- Process Owner
- Team Leader
- Team Facilitator
- Team Members
Before you begin
Determine candidates for standardization:
- Core Process
- Sub-Process
- Activities and Tasks
- Technology
- Unique Customer Services
Procedure Step Action 1 Click Standardization Matrix Template in Tools below. Result: File Download window pops up, asking the question, “Would you like to open the file or save it to your computer?”
2 Click Save. Result: Save As window pops up, prompting you to select a location in which to store the file.
3 Select a location in which to store the template and click Save. Result: Download Complete window pops up.
4 Click Open. Result: The template is opened, ready to be edited.
5 Does the list of SBUs in the “SBU” section need to be modified? · If yes, modify the list of SBUs in the “SBU” section to reflect your situation and then proceed to the next step.
Tip: Found in columns C through I.
· If no, proceed to the next step.
6 List Activities and/or Tasks in columns A and B. 7 In the “SBU” section, indicate with “Yes” or “No” whether the Activity/Task can be standardized. 8 For a “No” response, select a criterion from the drop-down list in the Differentiationsection, and explain in the Notes section. If you selected… Then … Regulatory/Legal Constraints Explain the prospect and timing of changing the constraint in such a way that allows for a common business process. Collective Bargaining Contract Constraints Explain the prospect and timing of changing the constraint in such a way that allows for a common business process. Local Physical Environment Fully document what it is about the local environment that prevents the adoption of a common process. Competitive Advantage Fully document the nature of the competitive advantage; quantify the financial value of the advantage; describe its sustainability under status quo; describe the impact on the competitive advantage of adopting a common process. Reference: Contact the appropriate Financial Director for assistance in documenting the financial value.
Consumer Expectation or Satisfaction Fully document the nature of the consumer expectation; quantify the financial value of satisfying the expectation at current levels; describe its sustainability under status quo; describe the impact to consumer satisfaction of adopting a common process. Reference: Contact the appropriate Financial Director for assistance in documenting the financial value.
Excessive Change Burden Fully document the financial impact of the change burden. Reference: Contact the appropriate Financial Director for assistance in documenting the financial value.
9 If a financial analysis was conducted, describe the results (i.e. Net Present Value, Payback period, etc) in column O of the Value section. Tools/Resources Standardization Matrix Template
Purpose
The goal!
To describe what the attributes of the process look like, after improvement, when the process is operating successfully.
Why do it?
Without a clear definition of what success looks like, the Process Improvement effort will not be able to show value to the organization.
What to do:
The Process Improvement Team needs to decide what success looks like when the Process is fully operational. This needs to be determined prior to full deployment.
Decision:
1) What needs to be measured and why?
2) How will it be measured?
3) What data needs to be captured? What will be done with the information?
4) What level of performance is desired?
5) What are the Performance Targets based on Benchmarking (Internal or External) data?
6) Are the measures balanced between cost, quality, cycle time and other important measures?
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Determine if benchmarking data is available for the process or any of its activities See Benchmark Resources in Tools below for assistance.
Determine if the success criteria will be qualitative or quantitative.
Procedure
Required Procedures
Based on the team Decision above, complete the following procedures:
- 1) For qualitative measures, complete Procedure 1 – Using the List Unique Criteria Tool.
- 2) For quantitative measures , complete Procedure 2 – Using the Key Performance Measures Tool.
Procedure 1 – Using the List Unique Criteria Tool
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To obtain permission to proceed on the project, based on analysis and a review of the Team’s work, and a high level description of the Should-Be process at the end of the project.
Why do it?
This ensures that senior management is supporting the work effort, resources and project timing.
This ensures that Process Owners and Resource Owners are in agreement of the project’s results.
This gives the team permission to proceed with the project.
What to do:
1) Use the presentation template below in the tools section and populate with the results of the Analyze and Identify activities. Most of the content should be derived from the As-Is Worksheet and reflect bias of the Sub-Process team.
2) Review analysis results and recommendations with the Process and Resource Owners, and upgrade as necessary.
3) Gain agreement from Process and Resource Owners to proceed.
4) Review findings with Process Council as appropriate.
Decision:
1) Do Process Owners and Resource Owners agree that this project is important, cost-justified, and budgeted?
2) Is there a clear signal to move the project forward?
Help: This step is an iteritative process. The team should develop the initial presentation and work with the Process Owner to fine tune it for the Process Owner to present to Resource Owners and other Process Owners as necessary for buy-in to move to the Design activity. This will help shorten the cycle time of the design activity by giving clear design criteria from the start of this activity.
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Process Owners
Resource Owners
Before you begin
The following analysis is completed:
- Process/Activity/Tasks defined
- Systems/Tools defiined
- Departments/Job Titles defined
- Breakdowns/Disconnects defined
- Cause/RootCause defined with key improvement recommendations
- Performance Metrics defined
- Standardization Matrix
|
||||
Purpose
The goal!
To adjust the Process Improvement Team in order to ensure that the appropriate stakeholders are involved in the continued re-design of the critical workflows.
Why do it?
This ensures that, if necessary, people with the additional information and expertise are included on the team(s) to expand coverage to these inter-related or broader processes and those members that are no longer needed are excused from future team activities.
What to do:
Consider who has been involved already and is no longer needed and any new people who should be involved now. The next series of tasks involves a lot of detail work and there may be key knowledge people who have not been involved to date and have a lot to contribute.
Decision:
1) Is the current direction of this Process Improvement activity aligned with the goals originally set forth?
2) Are the correct Team Members identified to deploy the Future State?
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Process Owners
Resource Owners
Before you begin
Burning Solutions have been identified and prioritized
| Procedure | ||||||||||||||||
|
| Tools/Resources |
| FrameTEC Team Charter AgendaTEC Template |
Purpose
The goal!
To obtain permission to proceed on the project, based on analysis and a review of the Team’s work, and a high level description of the Should-Be process at the end of the project.
Why do it?
This ensures that senior management is supporting the work effort, resources and project timing.
This ensures that Process Owners and Resource Owners are in agreement of the project’s results.
This gives the team permission to proceed with the project.
What to do:
1) Use the Business Case template below in the tools section, review each section and input your team’s response.
2) Conduct a Cost Benefit Analysis with your team for each benefit alternative described in the Business Case.
3) Review Business Case and Cost Benefit Analysis with your Process Owner.
4) Process Owner to review with Resource Owners, and Process Council once agreement and committment is in place give clear direction to the team to proceed with the Design activity.
Decision:
1) Do Process Owners and Resource Owners agree that this project is important, cost-justified, and budgeted?
2) Is there a clear signal to move the project forward?
Help: This step is an iteritative process. The team should develop the initial presentation and work with the Process Owner to fine tune for the Process Owner to present to Resource Owners and other Process Owners as necessary for buy-in to move to the Design activity. This will help shorten the cycle time of the design activity by giving clear design criteria from the start of this activity.
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Members
Process Owner
Resource Owner
Process Council
Before you begin
Developing a Business Case and Cost Benefit Analysis requires that any or all of the following circumstances must exist:
Implementation cost exceeds current signing authority.
Reduction in more than 5 employees requiring severence packages.
More that forty hours of programing required from IT.
Resource Owners are not in agreement with the identified opportunity due to lack of clarity of benefits.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
Get participants to understand the elements of the Design Activity and how the previous work prepares the team for this activity and following activities.
Why do it?
This activity helps to organize the team proactively and prepare them for the coming design work.
What to do:
Using the Design training module as a basis for educating the Process Improvement Team:
Modify the training Agenda.
Prepare to educate the team on the procedures and tools of the Design activity.
Decision:
1) Does the team understand how to implement the procedures and tools in the Design activity?
2) Does the team have an example specific enough to the process scope for them to continue through the analysis activity for the remaining processes?
Thoughts to convey:
“In the next activity, we see the development of the vision of the ‘Should-Be’ design, the enabling technologies, responsibilities and measurements.”
“The Design Activity uses the information from earlier activities to produce the plans for the Development Activity.”
Before you begin
Design team has been selected
Gate 3 has been successfully passed with Process and Resource Owners cleary in agreement and good direction provided to the team
| Procedure | ||||||||||||||||||
Help: For further Design training assistance, see Design training module via the Training side navigation selection. |
| Links |
 Design Activity Agenda Design Activity Agenda Design Presentation Design Presentation |
Roles and Responsibilities
|