Analyze
Description |
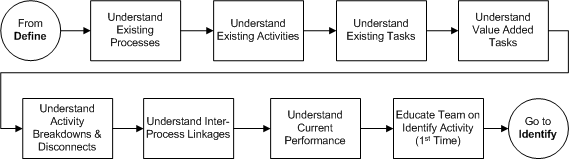
| Analyzing the current Processes, Activities and Tasks of the Improvement effort, leads to: a better understanding of how the identified process is interlinked with other processes. a clearer understanding of how the process currently works. whether or not the Tasks are value added. where there are breakdowns and disconnects.During the Analyze stage, two tools will be used: 1) The As-Is Worksheet – used to capture and document the process, activities, and tasks. Additionally, value-added tasks will be identified in the worksheet as well as breakdowns and disconnects. 2) FrameTec Problem Solving – used to capture performance measures and inter-process linkages.Help: Prior to working with the team on the following tasks, prepare a straw proposal of the process to be improved. If possible, prior to meeting, interview people individually to document and gain understanding of the process, activities, tasks and responsibilities associated with the process. Process Flow Diagram
|
In this diagram the Team meets to understand the existing process, what is/is not working, what is disconnected with other processes and performance in terms of quality, cost and time.
Procedures
Purpose
The goal!
To understand the processes targeted for improvement by defining the current work Process and / or Sub-Process.
Why do it?
Process analysis :
- Provides shared process knowledge
- Helps to avert mistakes
- Handles system constraints
- Builds on what works
- Gains consensus from the stakeholders involved
What to do:
Clarify the scope and purpose of each Process as it relates to the collective group involved in the improvement event.
Identify the primary contacts involved in this process that can be used to bring understanding to the team.
Capture terms & definitions that are used in the process to improve team understanding.
Decision:
1) Is each Process to be improved clearly defined?
2) Is the scope of the Process defined?
Responsibility
- Team Leader
- Team Facilitator
- Team Members
- Team Sponsors
Before you begin
Agreement on the Team Charter and Team Workplan have been reached
| Procedure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Help: Click Understand Existing Processes Example in Tools below to view a completed example of all the procedure steps. Copying and Pasting Ideas
|
| Tools/Resources |
| Process Improvement Team Charter Understand Existing Processes Example As-Is Worksheet Template |
Purpose
The goal!
1) To understand the current work Activities in preparation for:
Identifying solutions
Benchmarking
Integrating best practices
2) To describe in 7 plus or minus 2 statements “what activities” occur to complete the mission of the process.
Help: It is sometimes best to think in terms of outputs.
Why do it?
Activity analysis:
Provides shared process knowledge
Helps to avert mistakes
Handles system constraints
Builds on what works
Gains consensus from the stakeholders involved
What to do:
Capture and gain agreement on the existing Activities or deliverables for the identified process. The Activities should be in chronological or a logical order once identified.
Decision:
1) Is each Activity in the existing process clearly defined?
2) Are the Activities in chronological order?
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Complete Documenting Existing Process details in As-Is Worksheet
Procedure
Help: Click Understand Existing Activities Example in Tools below to view a completed example of all the procedure steps. |
| Tools/Resources |
| As-Is Worksheet Understand Existing Activities Example |
Purpose
The goal!
To capture and define the current work Tasks in preparation for:
Identifying recommendations
Benchmarking
Integrating best practices
Why do it?
Task analysis provides:
Shared process knowledge
Helps to avert mistakes
Handles system constraints
Builds on what works
Gains consensus from the stakeholders involved
What to do:
Tasks are individual units of work. The team should decide:
Who is responsible (by job title) for the Task
What department they are in
Decision:
1) Is each Task clearly defined?
2) Are Tasks sequenced in chronological order?
Help: When you cannot apply the chunking principal (7 plus or minus 2) to the number of tasks assigned to an activity, you should consider either combining or breaking out additional activities for the sub-process.
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Gain agreement on Process and chronological order of all Activities
Procedure
Required Procedures
Based on the team Decision above, complete the following procedures:
- 1) Identifying task descriptions
- 2) Identifying task responsibilities
Procedure 1 – Identifying task descriptions
Follow these steps to develop a description for each task of an activity:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To understand the nature of the Tasks, whether they add Value to the Activity or not.
Why do it?
Value Added Task Analysis captures the Process Team’s perspective, as well as provides immediate observation on potential opportunities for improvement.
What to do:
Once the Tasks and the details are identified for all Activities in the Process, ask the team to quickly run through the list of tasks and select from the drop down list whether the task is Value Added or Non-Value Added.
Decision:
1) Is each Task’s Value Added indicator assigned?
2) Are there any immediate incremental improvements we can make today that simplify and/or reduce effort in performing the task?
Responsibility
eam Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Complete listing of tasks under each activity in As-Is Worksheet.
Review presentation on Value Added Analysis.
|
||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To identify the Activity Breakdowns/Disconnects by defining the Existing Activity Situation.
Why do it?
Breakdown / Disconnect analysis provides:
Shared process knowledge
Helps to identify opportunities for improvement
Builds consensus from the stakeholders involved that change is needed
What to do:
Once the Activities have been identified, the next step is to identify and categorize breakdowns and/or disconnects. Reviewing the Change LevelsPresentation in Tools below will provide background information for understanding the categories of change and assistance in the categorization of breakdowns and disconnects.
Decision:
1) Are the nature of the Breakdowns and Disconnects understood and accurately documented?
2) Is there agreement on the identified Breakdowns / Disconnects?
3) Are the number of breakdowns and disconnects overwhelming the team? If so, use a pivot table in the As-Is Worksheet and calculate the percentages of breakdowns by category to determine which area to focus on during the Root Cause analysis in the Identify activity.
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Existing Activities are chronologically documented in an As-Is Worksheet.
| Procedure | ||||||||||
Help: Click Understand Activity Breakdowns and Disconnects Example in Tools below to view a completed example that illustrates the procedure steps. |
| Tools/Resources |
| As-Is Worksheet Understand Activity Breakdowns and Disconnects Example Change Levels |
Purpose
The goal!
To understand the process inter-linkages and to show how the key process is interrelated with other processes.
Why do it?
The key process under investigation may be so connected and/or interrelated with one or more other processes that they or some combination of processes become the scope for further inquiry.
What to do:
Before starting the design of the Should-Be process, it is important to understand the linkages between the processes being improved and those that will not be changed to avoid sub-optimization. Therefore, identify all existing linkages between defined processes.
Decision:
Have all linkages between the processes been identified?
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Before you begin
Process, Activities, and Tasks are documented and in chronological order.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Purpose
The goal!
To identify process improvement indicators.
Why do it?
Having a deep understanding of the decomposition of the process allows rapid diagnosis of what needs to be improved and the level of change necessary.
Example: People, Technology and / or Process
What to do:
Identify areas for incremental improvement by conducting any necessary studies and/or analysis.
Decision:
Do we understand enough about all facets of the process to begin defining the improvement?
If your process has been documented and improved recently and there is need to further improve but you don’t know where to begin, perform an Internal or External Benchmark study.
If your process is time sensitive to meeting customer expectations, perform a Cycle-Time Metrics Analysis (under column V in As-Is Worksheet).
If you are unclear of the cost basis of your process, perform an Activity Based Costing Analysis (under column AE in As-Is Worksheet).
If you have complaints from people receiving the output of your process, perform a Quality Analysis (These issues should surface during the Inter-Process Linkages discussion).
Responsibility
Team Leader
Team Facilitator
Team Members
Resource Owner(s)
Executive Committee
Before you begin
Value Added Analysis, Breakdowns / Disconnects are identified, and Inter-Process Linkages are complete.
Decide which analysis tool should be used to asses the current process performance.
Procedure
Required Procedures
Based on the team Decision above, complete one or all of the following procedures:
- 1) Internal or external benchmark study
- 2) Cycle-time metrics analysis
- 3) Activity based costing analysis
- 4) Quality analysis
Procedure 1 – Conducting an internal or external benchmark study
Follow these steps to complete an internal or external benchmark study:
Procedure 2 – Performing cycle time metrics analysis
Follow these steps to identify the task frequency, batch size, time required, and time measurement aspects necessary to perform the analysis:
Help: Click Understand Current Performance – Cycle Time Metrics Analysis in Tools below to view a completed example of procedure 2. Procedure 3 – Performing activity based costing analysis Follow these steps to complete the aspects necessary to perform the analysis:
Help: Click Understand Current Performance – Cycle Time Metrics in Tools below to view a completed example of procedure 3. Procedure 4 – Performing a quality analysis Follow these steps to test the output of your process through a quality analysis: |
| Tools/Resources |
| As-Is Worksheet Understand Current Performance – Activity Based Costing Analysis ABC Analysis Training Understand Current Performance – Cycle Time Metrics Analysis |
Purpose
The goal!
Get participants to understand how to identify the root causes of problems, prioritize some recommendations and develop standardization and success criteria, prior to beginning the Identify activity.
Why do it?
This activity helps to organize the team and prepare them for the coming identification work.
What to do:
Using the Identify training module as a basis for educating the Process Improvement Team:
Modify the training Agenda.
Prepare to educate the team on the procedures and tools of the Identify activity.
Using the process scope section of the Team Charter, select a section of process work to demonstrate what needs to be done and how to do it.
Decision:
1) Does the team understand how to implement the procedures and tools in the Identify activity?
2) Does the team have an example specific enough to the process scope for them to continue through the identify activity for the remaining processes?
Thoughts to convey:
“In the next activity, we will identify what needs to be improved and we will see some measurement devices and success criteria.”
“Quite often, Root Causes of problems are only identified after a fair amount of examination and questioning.”
“After prioritizing the recommended solutions, some will be recognized as ‘quick fixes’. These are solutions that can be implemented quickly, don’t cost much, and can result in immediate positive results.”
Before you begin
All Analyze tasks are complete
|
||||||||||||||
Roles and Responsibilities
|